🎩 Top 5 Security and AI Reads - Week #28
Adversarial model manipulation, autonomous cyber attack agents, memory-based malware detection, robustness evaluation frameworks, and reinforcement learning for vulnerability detection
Welcome to the twenty-eighth instalment of the Stats and Bytes Top 5 Security and AI Reads weekly newsletter. We're opening with a dive into how mechanistic interpretability can expose and exploit internal reasoning processes in LLMs, demonstrating jailbreak techniques that target refusal directions during Chain of Thought processing. Next, we examine a framework for autonomous multi-host network attacks that dramatically improves LLM performance by splitting planning and execution into specialised agents, achieving 3-4x better results across benchmark environments. We then explore a new dataset of malware memory snapshots that provides researchers with the complete toolkit needed for volatility analysis and malware detection validation. Following that, we investigate a rigorous evaluation framework for adversarial robustness tests that exposes significant discrepancies between attack implementations and introduces novel optimality metrics for comparing gradient-based attacks. We conclude with an innovative approach to fine-tuning LLMs for vulnerability detection using Group Relative Policy Optimisation, delivering substantial improvements across multiple models and datasets through dynamic reward functions that balance formatting, correctness, and reasoning.

A note on the images - I ask Claude to generate me a Stable Diffusion prompt using the titles of the 5 reads and then use the FLUX.1 [dev] on HuggingFace to generate it.
Read #1 - Adversarial Manipulation of Reasoning Models using Internal Representations
💾: GitHub 📜: arxiv 🏡: ICML 2025 Workshop on Reliable and Responsible Foundation Models (R2FM)
This is a grand read for folks interested in ways mechanistic interpretability can be used to identify interesting things about the internals of models.
Commentary: I enjoyed this paper. The authors identify that DeepSeek-R1-Distil-Llama-8B determines if a refusal response will be outputted during the Chain of Thought (CoT) stage. This kind of makes sense to me given that these reasoning models are trained to formulate the response and generate supporting information prior to providing the actual output. There is an example in the paper where the model basically says, “This prompt looks funny given I have been asked a question about another topic!” The authors then come up with a method of removing this direction (by what I think is activation patching) and find they can effectively jailbreak a model by targeting this refusal direction.
The authors identify a couple of limitations of the work that I noted down as I read it. The paper only targets one model. It would be cool to see if these results translate to all/most CoT-style models. And the evaluation is done effectively in a one-shot, dataset-wise. This means that the variability of model outputs (due to temperature) is not captured. It would be cool to see this research run again but across N outputs to see if the model is consistent in this behaviour.
The authors pull out a potential future research direction that is cool – if the CoT models are a bit suspicious of dodgy inputs, can we identify that suspiciousness?
Read #2 - On the Feasibility of Using LLMs to Autonomously Execute Multi-host Network Attacks
💾: N/A 📜: arxiv 🏡: Pre-Print
This is a cracker of a paper for folks interested in autonomous cyber attack agents and how various bits and pieces can be used together to make something very cool!
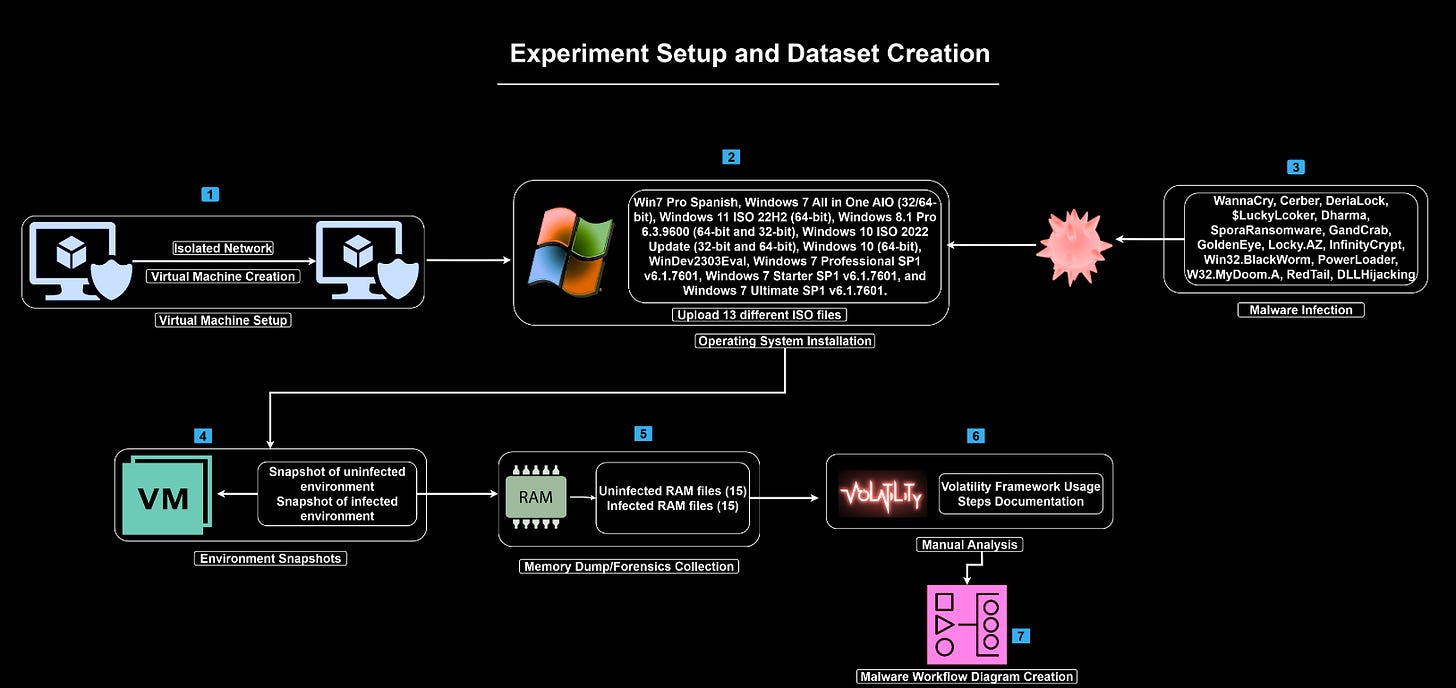
Commentary: This paper is a double whammy – a benchmark and an approach to multi-box attacks. I’ll start by saying that there is a statement in the paper that suggests the authors are going to drop everything open source, but I have been unable to actually find it. Drop the code, drop the code!
Anyways, turning first to the benchmark. The benchmark is made up of 10 environments of varying complexity and objectives. It is fairly unclear from the paper what these environments are. Are they VMs, containers or what? Reading the appendix doesn’t help too much, but a lot of Python code snippets are provided. I can infer a little bit from them and think it may be a Python wrapper over something like LibVirt, maybe. They do state that Windows is not supported, which is not overly surprising because starting up and resetting Windows machines is a right pain and takes too long!
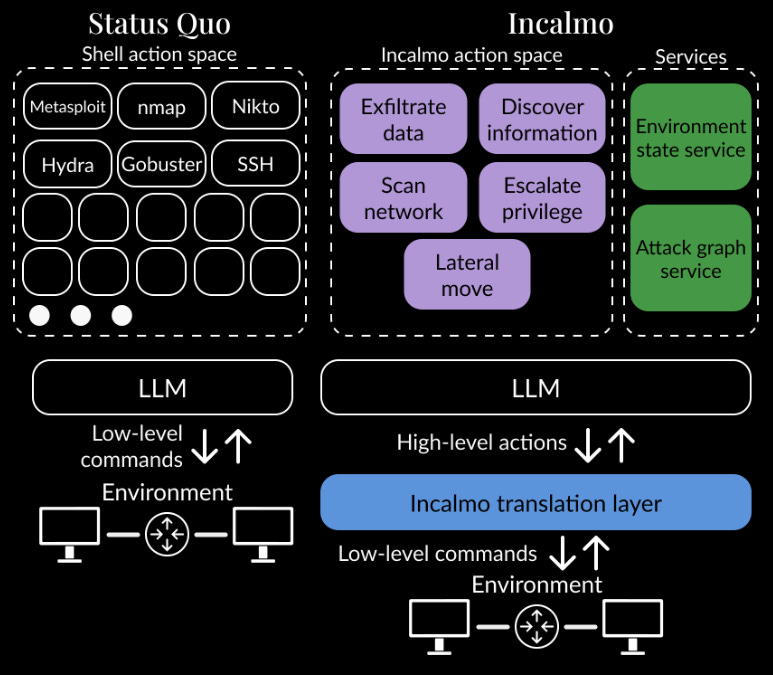
There is a lot more information provided for the approach, which I think is pretty damn awesome! Rather than providing the LLM with very low-level tools such as executing shell command X or Y, the authors instead create a series of high-level tasks which is used by the Planner Agent. Once a high-level task has been chosen (such as “Scan the external network”), this command is then passed to a specialist “Scanner Agent” which completes the objective of scanning the network before returning the output. This makes a lot of sense to me, as you can refine the system prompt for the specialist agents with things such as example commands or guides. It is, however, slightly murky in the paper whether these specialist agents are actually LLMs at all or basically just scripts. Either way, the approach basically splits planning and doing into two discrete tasks.
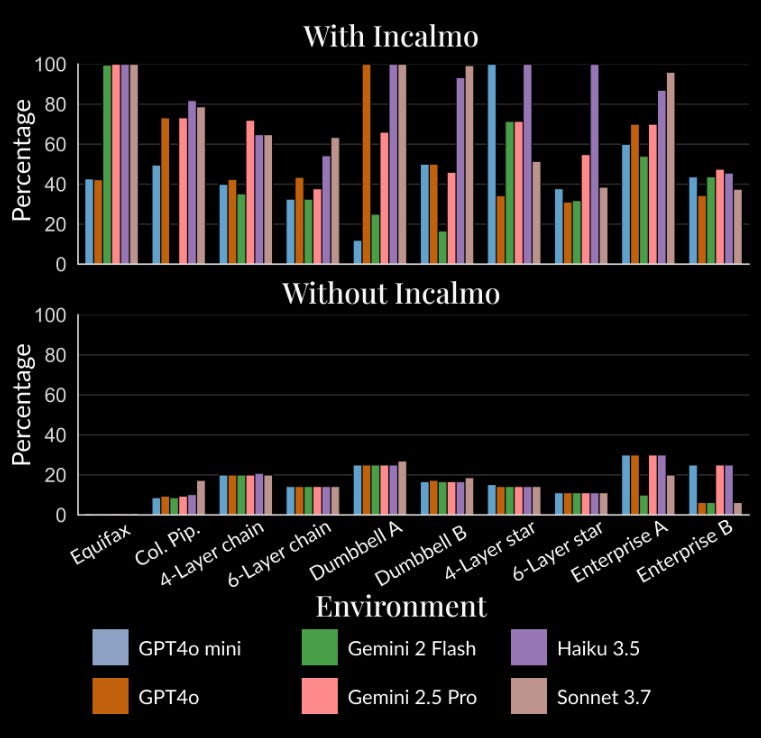
There is a fair bit of evaluation which is worth digging into if you are really interested, but the plot below speaks for itself. Using this framework with several frontier models almost 3-4x’s performance across the board! Barmy!
Read #3 - MalVol-25: A Diverse, Labelled and Detailed Volatile Memory Dataset for Malware Detection and Response Testing and Validation
💾: IEEE DataPort 📜: arxiv 🏡: Pre-Print
This should be a quick but grand read for folks interested in using memory snapshots to support malware detection as well as folks interested in applying RL to this problem.
Commentary: This paper introduces a new dataset of malware memory snapshots as well as what looks like VM images. It is fairly small with only 15 samples but does include what looks like the whole kitchen sink (memory snapshot pre/post infection, VM images, etc.). The methodology looks solid, and this dataset could be of interest to folks, especially those looking for examples to learn/use volatility with!
Read #4 - Evaluating the Evaluators: Trust in Adversarial Robustness Tests
💾: GitHub Blog 📜: arxiv 🏡: Pre-Print
This should be a grand read for anyone interested in gradient-based adversarial attacks and how to cross-compare the efficacy of attacks.
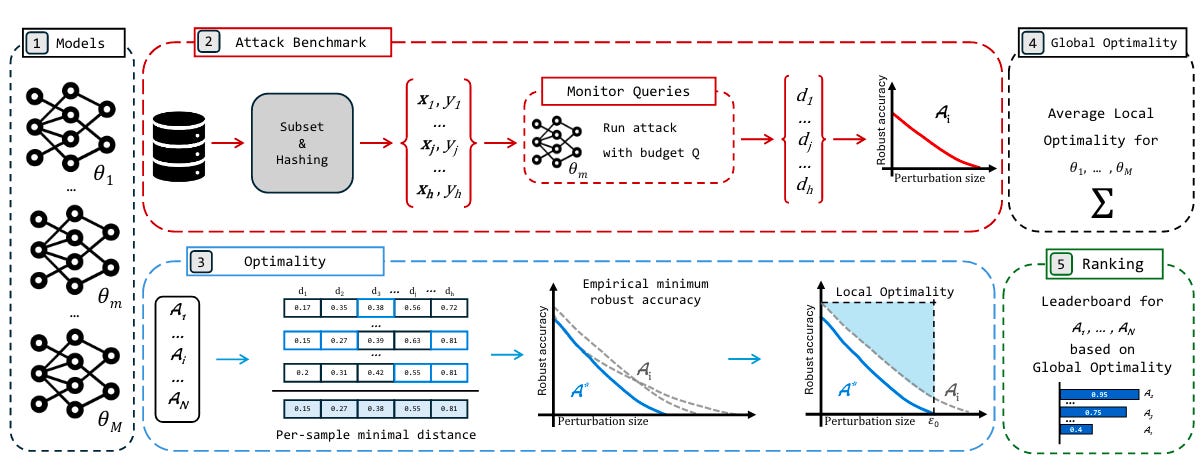
Commentary: This paper is fantastic and short. It focuses specifically on gradient-based attacks. Some may feel that real attackers are unlikely to use these sorts of attacks in practice (because it relies on direct model access), which is true. That being said, using gradient-based attacks for your own testing is wholly sensible, as they can be viewed as “worst-case” tests.
The paper itself comes up with an “optimality” metric and uses this to rank attacks. This “optimality” metric is calculated locally and globally. At the local level, the optimality metric is the difference between areas of a given attack versus the best-known attack’s area. This area is drawn similar to Area Under the Curve (AUC) but uses robust accuracy and perturbation size instead. At the global level, the optimality score is an aggregate of local scores across all models. This provides a global optimality score for a given attack.
The benchmarks website is great too and has some very interesting results to look at. These are briefly summarised in section 3. 2 main take-home messages and is well worth a read. I was drawn to effectiveness vs efficiency tradeoffs and implementation validity/pitfalls. For the Effectiveness vs Efficiency Tradeoffs, it’s interesting that the authors have found some methods that are very quick but fail sometimes vs some that are rock solid but take ages. For anyone who has made adversarial examples, you’ll know the pain of doing 1000s of the bloody things. For the implementation bits, this paper’s methodology demonstrates something I think folks have known for a while – these adversarial attack libraries are a bit ropey! The authors find large discrepancies between libraries implementing the same attack, with some differences causing 65% ASR differences… bonkers.
Read #5 - Improving LLM Reasoning for Vulnerability Detection via Group Relative Policy Optimization
💾: N/A 📜: arxiv 🏡: Pre-Print
This should be a great read for folks interested in fine-tuning LLMs to get better at vulnerability detection.
Commentary: I found this paper towards the tail end of the week and have not had a chance to properly dig into the details, but there are several cool things I have spotted. Firstly, the authors come up with a GRPO reward function that rewards the model across 3 different areas: formatting, correctness and reasoning. This is then tweaked with a dynamic reward function to avoid reward hacking.
The authors then do a tonne of experiments comparing GRPO to SFT and with and without reasoning. This culminates in the monster table on pg. 14, which is impressive to say the least! There is essentially a large % improvement across basically all datasets for all 3 models fine-tuned (Qwen-2.5, LLaMA 3B, LLaMA 8B). One thing that I didn’t manage to dig out of this paper was – ok, it improves a lot, but was it really shit to begin with? I guess I’ll need to read it a second time!
That’s a wrap! Over and out.